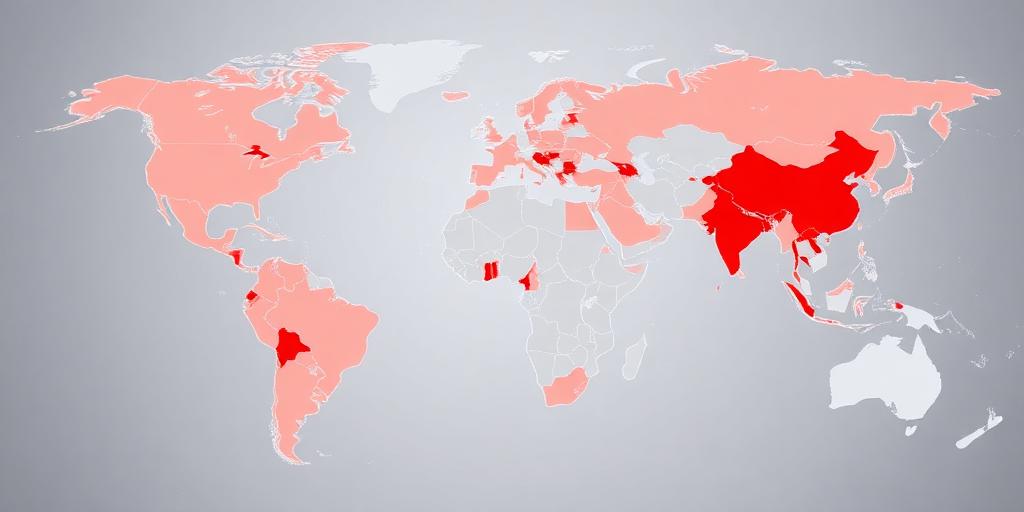
Each year, Freedom House releases its "Freedom on the Net" report, offering a comprehensive assessment of internet freedom around the globe. The 2023 report provides a sobering look at the state of online censorship and digital rights. This article breaks down the key findings, spotlighting the countries with the most restricted internet environments and analyzing the trends driving these limitations.
Key Findings of the 2023 Report
The 2023 "Freedom on the Net" report indicates a continued decline in global internet freedom. Several factors contribute to this trend:
- Increased Government Control: Many governments are tightening their grip on online content, using various methods to suppress dissent and control the flow of information.
- Sophisticated Surveillance Technologies: Advanced surveillance tools enable authorities to monitor and track citizens' online activities, leading to self-censorship and fear of reprisal.
- Disinformation and Propaganda: State-sponsored disinformation campaigns are becoming increasingly prevalent, undermining trust in legitimate news sources and manipulating public opinion.
- Website Blocking and Content Removal: Blocking websites and demanding the removal of content remain common tactics used by governments to stifle free expression.
- Crackdowns on Social Media: Social media platforms are under increasing pressure to censor content and cooperate with government requests for user data.
Countries with the Most Censored Internet Environments in 2023
The report identifies several countries where internet freedom is severely restricted. These nations employ a range of tactics to control online content and suppress dissent.
- China: China remains the world's worst abuser of internet freedom. The government maintains a sophisticated system of censorship, surveillance, and control, often referred to as the "Great Firewall."
- Myanmar: Following the 2021 coup, Myanmar has dramatically curtailed internet freedom. The military junta has imposed strict censorship, blocked social media platforms, and arrested individuals for their online activities.
- Iran: Iran's government heavily filters online content, particularly social media and news websites. Authorities also monitor and prosecute individuals for expressing dissenting opinions online.
- Vietnam: Vietnam's internet environment is tightly controlled by the government, which requires social media companies to remove content deemed critical of the state. Independent journalists and bloggers face harassment and imprisonment.
- Russia: Russia has ramped up its efforts to control online content and suppress dissent. The government has blocked numerous websites, imposed hefty fines on social media companies that fail to comply with its demands, and targeted activists and journalists.
Methods of Censorship
Governments employ various methods to censor online content and restrict internet freedom:
- Website Blocking: Blocking access to websites that are deemed critical of the government or that provide information that the government wants to suppress.
- Content Removal: Ordering social media companies and other online platforms to remove content that violates government regulations.
- Surveillance: Monitoring citizens' online activities to identify and punish those who express dissenting opinions.
- Internet Shutdowns: Shutting down internet access during times of political unrest or protest.
- Legal and Regulatory Frameworks: Enacting laws and regulations that restrict online expression and give the government broad powers to control online content.
Implications and Consequences
The decline in internet freedom has far-reaching implications. It not only restricts citizens' access to information and their ability to express themselves freely but also undermines democracy and human rights. The consequences include:
- Suppression of Dissent: Online censorship prevents citizens from expressing dissenting opinions and holding their governments accountable.
- Erosion of Democracy: Internet freedom is essential for a healthy democracy. When citizens are unable to access information and express themselves freely, it undermines the democratic process.
- Human Rights Violations: Online censorship violates fundamental human rights, including the right to freedom of expression and access to information.
- Economic Impact: Restricting internet freedom can also have a negative impact on economic development, as it stifles innovation and limits access to global markets.
Conclusion
The 2023 "Freedom on the Net" report paints a concerning picture of the state of internet freedom around the world. As governments continue to tighten their grip on online content, it is crucial to defend digital rights and promote policies that protect internet freedom. By raising awareness, advocating for policy changes, and supporting digital activists, we can work towards a more open and democratic internet for all.